In the case of Linux, the swap file is an important part. It’s not a must-have option but having one is crucial for a number of purposes. Generally, when installing the system, you have to declare the size of the swap file. The recommended size is 4GB but you can either decrease or increase it depending on your demand. Today, let’s have a look at changing the swap size in Ubuntu.
Note – Running all these commands require root privilege, so I recommend running a “root” terminal.
root@sv0:~# sudo -sFinding out available swap file(s)
Before we get to change the swap, let’s find out how much swap size we have.
root@sv0:~# swapon -sAccording to the result, the system has a swap file at “/swapfile”.
For manipulating the swap file, we have to disable it first.
root@sv0:~# swapon -a
Now, change the size of the swap file
root@sv0:~# dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1M count=4096
Here, the total size of the swap file will be bs*count = 1M x 4096 = 4GB
Make the “/swapfile” usable again –
root@sv0:~# mkswap /swapfil
Turn on the swapfile –
root@sv0:~# swapon /swapfile
After restarting your system, check out the result –
root@sv0:~# swapon -s
Deleting the swap file
If your RAM space is high enough, then you probably want to get rid of the swap file. If that’s your case, then let’s get rid of the swap file!
Don’t worry! I’ll also show you how to set a completely fresh swap file.
For deleting the swap file, run the following commands –
root@sv0:~# swapoff -v /swapfile
Remove the swap file entry from “/etc/fstab” file. It should be the last line of the file.
root@sv0:~# gedit /etc/fstab
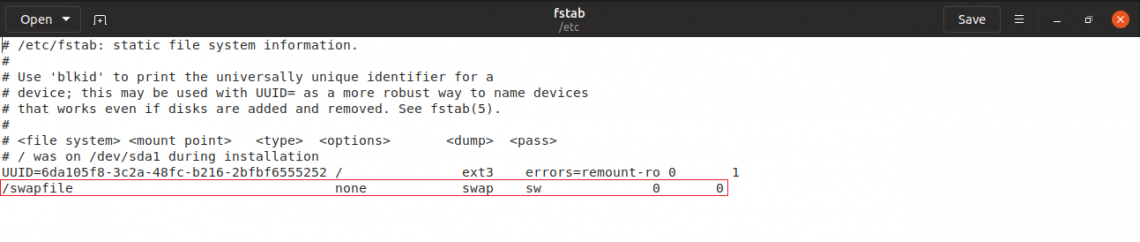
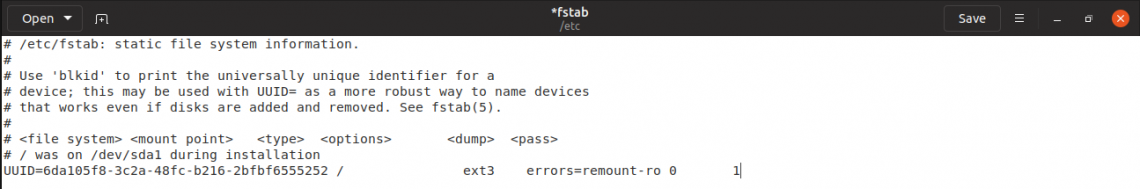
Now, time to remove the actual swap file.




 e poi
e poi